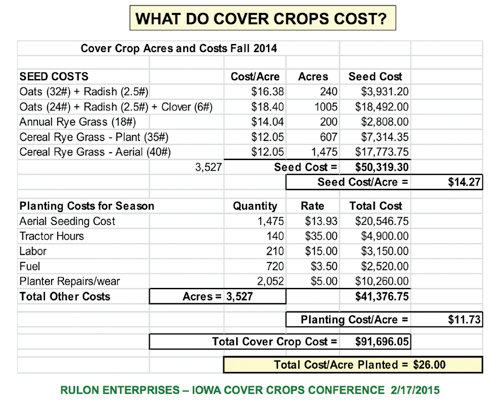
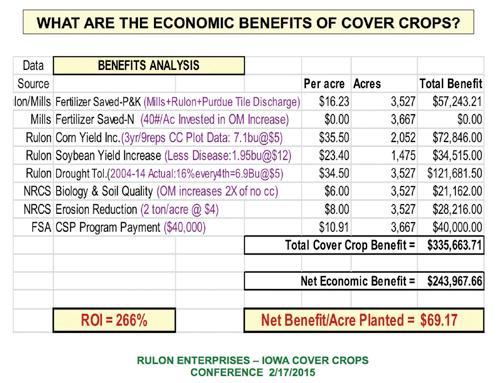
Ron Althof is an agronomist and cover crop seed specialist working out of Effingham, Illinois. In a recent conversation, he talked about the value of cover crop mixes. And while some “cocktail” mixes can contain more than a dozen different species…and cost upwards of $60/acre to plant, he suggested starting with more basics, especially if you’re new to using cover crops.
“More people this past year tried rapeseed (or “rape”) in combination with annual ryegrass,” Ron said. “The two work together very well and the cost per acre is about a third of what expensive cocktail mixes cost.” Annual ryegrass goes on at a rate of about 15 – 20 lbs/ac, depending on whether you’re drilling (less seed) or broadcasting it. Rapeseed goes on at a rate of about 2 lb/ac.
The value of annual ryegrass, of course, is its ease of germinating and growing, whether drilled after harvest or broadcast before harvest. Annual ryegrass has deep penetrating roots, as well as a large surface mat, all of which promotes soil stability and friability (crumbly texture), with more organic matter (from decaying roots after the ryegrass is killed in the spring) and attractive microbiology (healthy bacteria, earthworms, etc).
Rapeseed is a major crop worldwide, used for oil production (vegetable and biodiesel) and as meal for livestock. In recent years, rape has been successfully used as a cover crop as well. Ron mentioned some of its attributes:
“Rapeseed also broadcasts easily and establishes well,” Ron added. “It can be planted later than radish. Like a radish, rape also has a nice tap root; but its advantage over radish is that rape has strong lateral branching roots, whereas Radish has only small lateral root hairs. Thus, the rape root stays in the ground. The other nice thing: rape usually doesn’t winter kill. It’s hardy, like annual ryegrass, and thus will protect soil from winter and spring erosion and runoff problems.”
“Finally, rape and annual ryegrass is a great cover crop mix to use whether your next crop is soybeans or corn. Annual ryegrass is a perfect choice for sequestering nitrogen, useful to both beans and corn in July when the nitrogen is released by the decaying cover crop residue. Rapeseed also helps soybean foliage as the cover crop residue releases carbon dioxide. In the process, rape also seems to protect soybean plants from nematode infestation and sudden death syndrome.”
One final note from Ron: “When terminating rapeseed, the appropriate herbicide to use is 2, 4-D…glyphosate alone will not provide a good kill.”